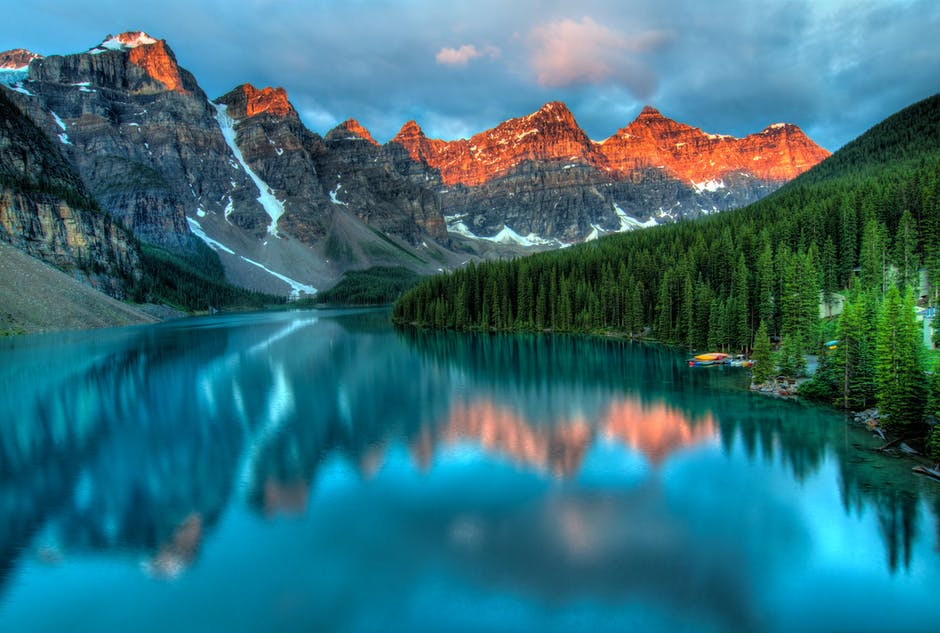
The lake at 12,500 feet (3,810 meters) in the Andean Mountains of Peru straddles the international border between Peru and Bolivia. Titicaca is the second South American lake to be the biggest (after Maracaibo). It encompasses around 3,200 square miles (8,300 square kilometers) (190 km). It is 80 kilometers from one end to the other end. A straight on the lake separates the two bodies of water into two halves. The largest, in the northwest, is called Lake Grande in Bolivia.
Name Origin

Titicaca is a mystery name because it has been interpreted as Lead Rocks and Rock of the Puma. Titicaca is located in a huge inland Andean basin that includes the entire Altiplano (highland) in the Andes. At an elevation of 21,000 feet, the highest points of the Andes range in the Cordillera Real, on the northeastern (or Bolivian) shore of Lake Cachora, several of them have glaciers that are a great deal higher than that (6,400 meters).
On average, the lake is 460 to 600 feet (140 meters) deep, although the deepest point is 920 feet (280 meters) off Isla Soto, which is found near the lake’s northeast end.
One river, the Ramis, drains two-fifths of the entire Titicaca lake. The southern end of the lake is fed by one little river that carries the given name of Desaguero. This outflow only pulls water from 5 percent of the lake; the rest evaporates in the dry Altiplano winds.
Titicaca’s Lake
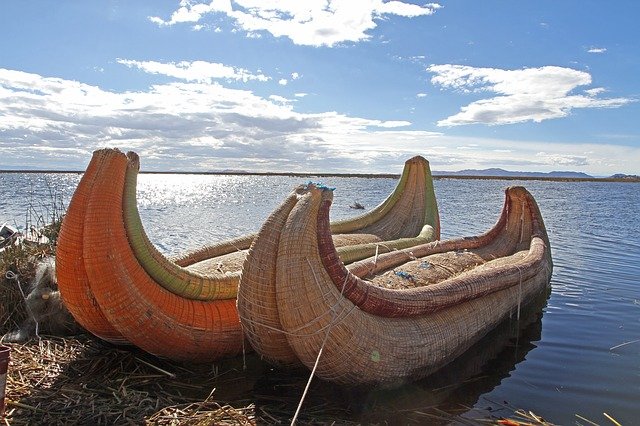

Titicaca’s level can rise and fall according to year-to-to-to-year patterns. The lake’s level rises during the rainy season (December to March, to go down in the dry months). Titicaca was assumed to be in the past to be on the decline, but recent investigations show that it is very consistent with a regular rise and decrease.
The waters of Titicaca have a low mineral content and are watery and slightly salty. The salinity is between 5.2 and 5.5 parts per thousand. At 56 °F (14 °C), the temperature on the ground varies from 66 feet (20 m) to 52 °F (23 C), along with the entire depth of the pond. analyses have shown amounts of NaCl, CaSO4SO4, and MgSO4 in the water
In large part, the life of Lake Titicaca’s fauna is composed of two distinct species of fish—usually striped or barred with black—and those that devour kill anything that crosses its path (Trichomycterus). Around 1939, trout were introduced into the Lake Titicaca basin. The lake attracts huge frogs that can grow up to nearly a foot long.
Titicaca is a landlocked lake. Forty-one of its islands, some of them heavily populated, rise above the surface of the water. Its name means “Island of the Sun” in the Sun.”
Conclusion:
Even though the Aymara agriculture dates back to the Inca era, barley, which originated in the high Andes, quinoa (a kind of weed), and potato, originated in the Bolivian plateau. In actuality, the highest possible plot was located near Titicaca—a meadow of barley that grew up to 15,420-metreemet (4,700 m) altitude. Up at this elevation, camel relatives for the Amerindians, the grains never get to mature, but alpaca and llamas perform their other functions of animals of burden and supply them with meat and wool remain edible. Because the land is heavily pre-Columbian, it contains enormous numbers of raised fields and ditches, which were once used to aid drainage and increase agricultural production—resurrected from its old state in Peru and Bolivia.